
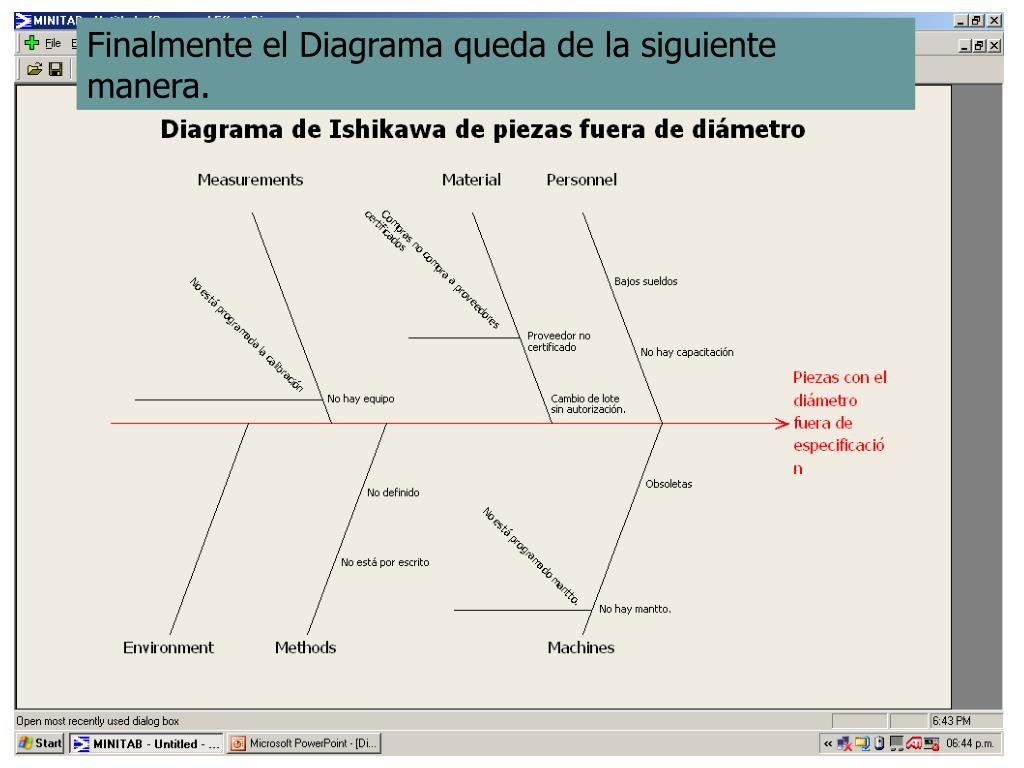
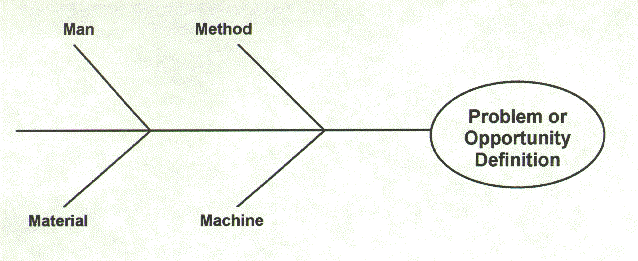
Layers of branches indicate causal relationships. Continue to ask “Why?” and generate deeper levels of causes. Write sub–causes branching off the causes. Ask the question “why does this happen?” again.Causes can be written in several places, if they relate to several categories. Ask: “Why does this happen?” As each idea is given, the facilitator writes it as a branch from the appropriate category. Write the categories of causes as branches from the main arrow.For instance, it might make sense to start with these generic headings: methods, machines (equipment), people (manpower), materials, measurement, and environment. Brainstorm the primary categories of causes for the problem.Write the problem statement at the center-right of the flipchart or whiteboard, box it, and draw a horizontal arrow running to it.The group should agree on a problem statement (effect).The purpose of the Ishikawa diagram is to allow management to determine which issues have to be addressed in order to gain or avoid a particular event. Este diagrama se fundamenta en la idea de que los problemas se resuelven ms favorablemente al identificar y corregir las causas de raz del problema, en lugar de centrarse en sus sntomas. They are causal diagrams created by Kaoru Ishikawa to show the causes of a specific event. They resemble a fish skeleton, with the "ribs" representing the causes of an event and the final outcome appearing at the head of the skeleton. El diagrama de Ishikawa, es una herramienta de la Calidad que facilita la identificacin de las causas de los problemas o incidentes detectados. Ishikawa diagrams are sometimes referred to as fish bone diagrams, herringbone diagrams, cause-and-effect diagrams, or Fishikawa. Ishikawa diagrams often follow the "Six M's": manpower, machinery, methods, materials, measurement, and mother nature.Shaped somewhat like a fish, these charts are sometimes called fishbone or "Fishikawa" diagrams.They are named after Japanese engineering professor Kaoru Ishikawa in the 1960s, who helped apply them to manufacturing processes.An Ishikawa diagram is used to show the causal factors that go into some final outcome, often related to a production or design problem. El objetivo de esta sptima edicin de Estadstica para administracin y economa es crear un libro que resulte amigable para los estudiantes de estadstica y donde los profesores que imparten la ctedra encuentren material suficiente para adaptar el curso de acuerdo a sus necesidades.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
